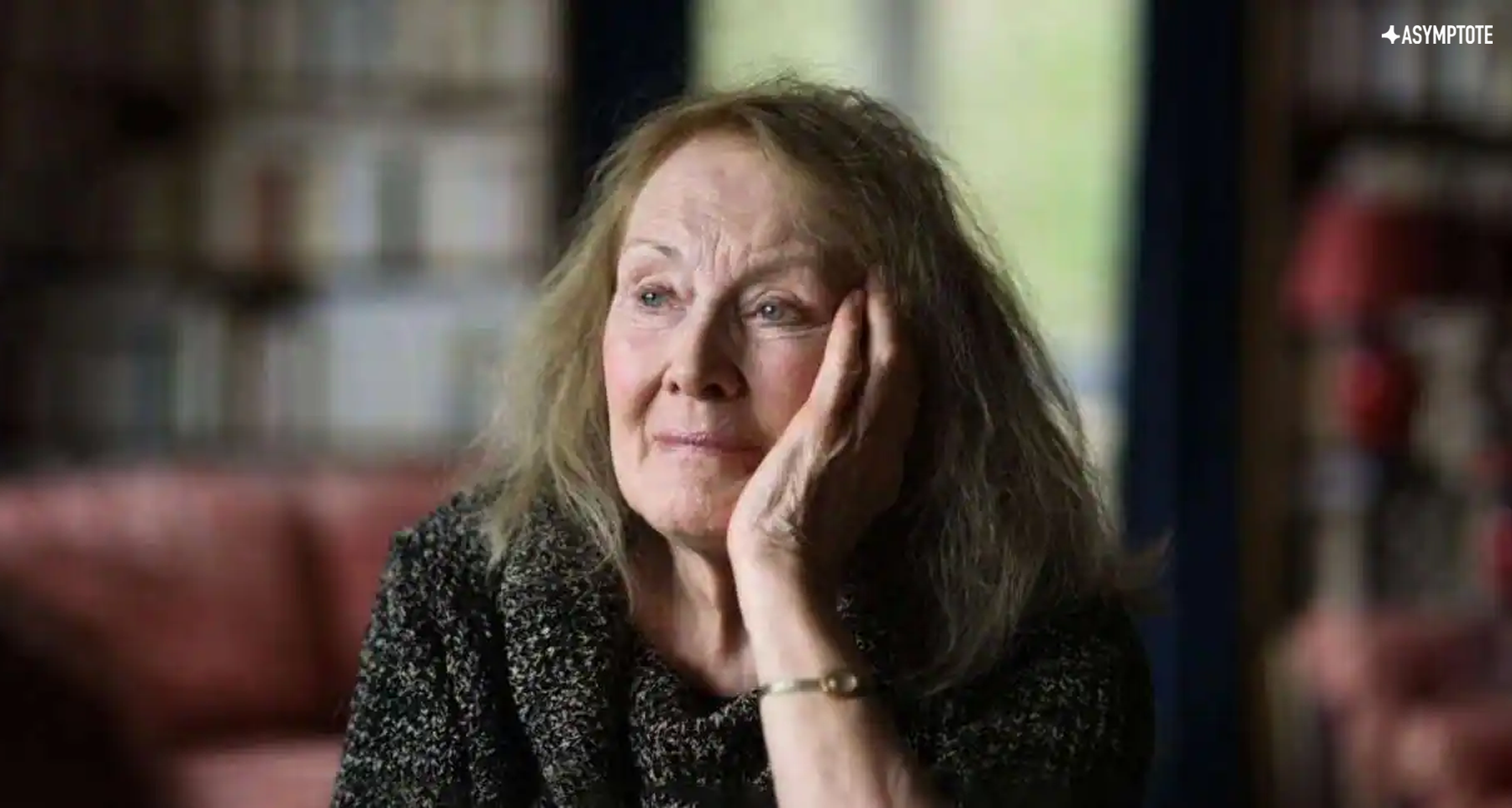
Jon Fosse’s A Shining is both a luminous entryway for newcomers to the Norwegian author, and a fine distillation of Fosse’s long-running themes for familiar fans. We are proud to feature this latest English offering of the Nobel laureate as our October Book Club selection, and in this monthly interview with the translator, Damion Searls talks to Georgina Fooks about following rhythms, the translator as reader, and making his own rules.
The Asymptote Book Club aspires to bring the best in translated fiction every month to readers around the world. You can sign up to receive next month’s selection on our website for as little as USD20 per book; once you’re a member, join our Facebook group for exclusive book club discussions and receive invitations to our members-only Zoom interviews with the author or the translator of each title.
Georgina Fooks: To begin, congratulations on the Nobel Prize! I know the Swedish Academy likely would have been reading Fosse in Norwegian, but there’s no doubt that your translations of Fosse into English have been so important for the increased critical reception of his work.
Damion Searls: Thank you! Something that’s worth telling people who aren’t in the book business – I know Asymptote is well aware of this – is that for better or for worse (mainly for worse), English is the language that matters professionally for world literature. A German publisher told me a couple of years ago that if they have a book, they can get it translated into five or six languages, but it’s not until it gets a review in the Guardian UK or in the New Yorker that they can sell it to twenty or thirty languages—and they also told me that this is increasingly the case. English really is the gateway to bigger success for every other language; it’s not going to be a worldwide, translated-everywhere success unless it goes through English first.
The thing about Fosse—which Americans and English audiences don’t really know—is that he’s incredibly famous worldwide as a playwright. He is, from what I’ve read, the most produced playwright alive today. There have been productions of his plays in fifty languages all over the world, and it’s just never taken off in England or America. And there is a question asked about Fosse’s work: is it inaccessible? Well, if he’s the most produced playwright in the world, then by definition, it’s accessible. He was honoured with many prizes in Europe and in Norway before the English translations.
It’s not the case that the English publication raised him from obscurity, but it does seem to be a kind of stepping stone to things like the Nobel or to more translations. I know that now, Septology is being sold to dozens more languages than it had been before. READ MORE…