The allure of Eileen Chang’s prose is a bewitching combination of insight and precision—sensual acuity married with an editorial scrupulousness. Earning widespread renown with renderings of the delicate, tenuous relationships in the volatile societies of her time, Chang has become known for her ability to create vivid, lasting images. It’s no wonder, then, that her works have served as the material for several celebrated films; today, our blog editors are taking a look at Hong Kong director Ann Hui’s adaptation of Chang’s rich novella of courtship and compromise, Love in a Fallen City (1984). What follows is a discussion on the transposition of Chang’s “cinematic” language, the pitfalls of overly faithful adaptation, and the difficulties of portraying interiority.
Shawn Hoo (SH): I have always thought of Eileen Chang’s prose style—her montage of overlapping timelines; her patient, exquisite visualising of scenes; her keen ear for dialogue—as having an affinity with the language of film. That is, her stories come to me almost ready-made for film. Unsurprisingly, Chang herself did write fourteen screenplays (a neglected part of her oeuvre), and several of her stories have been adapted by celebrated Sinophone filmmakers such as Stanley Kwan, Ang Lee, Hou Hsiao-hsien, and of course, Ann Hui (all of whom have no doubt disseminated Chang’s legacy to new audiences). A literary style that lends itself so naturally to cinema has its pleasures and, in some cases, its perils when it comes to adaptation. Just hear what Hui admits when asked about her interpretation of Chang’s story: “There is no interpretation at all,” she says, “It’s more a representation. The novel is so good that adding anything at all seems impossible.” If by “representation” Hui means to hew close to the original text, then this bears out in the film’s dialogue, which is used almost verbatim in its Cantonese translation, as well as in its rendering of key scenes which appear largely unmodified on screen. Consequently, what is arguably Chang’s most loved story has had a relatively lukewarm reception in its filmic context (and in Hui’s otherwise prolific oeuvre). Faithfulness—that contested word so frequently used to discuss translation—it seems, does not always reward.
This for me raises questions about the merits of transferring what is ostensibly cinematic writing onto the film medium, and how their relationship—as well as mutual realisation—can be understood beyond a scene-for-scene, image-for-image correspondence, which is at least how I conceive of Hui’s approach: too faithful. To be clear, there is much to admire in this film, especially Hui’s treatment of early 1940s Shanghai and Hong Kong. Whereas the former has the camera concentrated on the decaying, claustrophobic Bai household and moves between adjacent rooms only to hear Liusu’s relatives badmouthing her, the latter moves liberally between the historic Repulse Bay Hotel, couples dancing to a jazz number at the Hong Kong Hotel, outdoor Chinese opera, and a rendition of Greensleeves all heard while Liusu and Liuyuan walk the city. The film’s construction of these two settings dramatises the shifts in Liusu’s psychology, one that liberates her from the sad huqin of an insular household into the cacophonous colonial cosmopolitanism of British Hong Kong which signifies new beginnings. Or rather, three settings: if we distinguish Japanese-occupied Hong Kong for its distinct aural and visual qualities. Here, I think Hui successfully leverages on the medium to elaborate on Chang’s vision, that is the role of contingency—of situated time and place—to precipitate love.
At this point, I wonder if either of you might have a different take on the relationship between representation and interpretation, to borrow Hui’s own distinction?
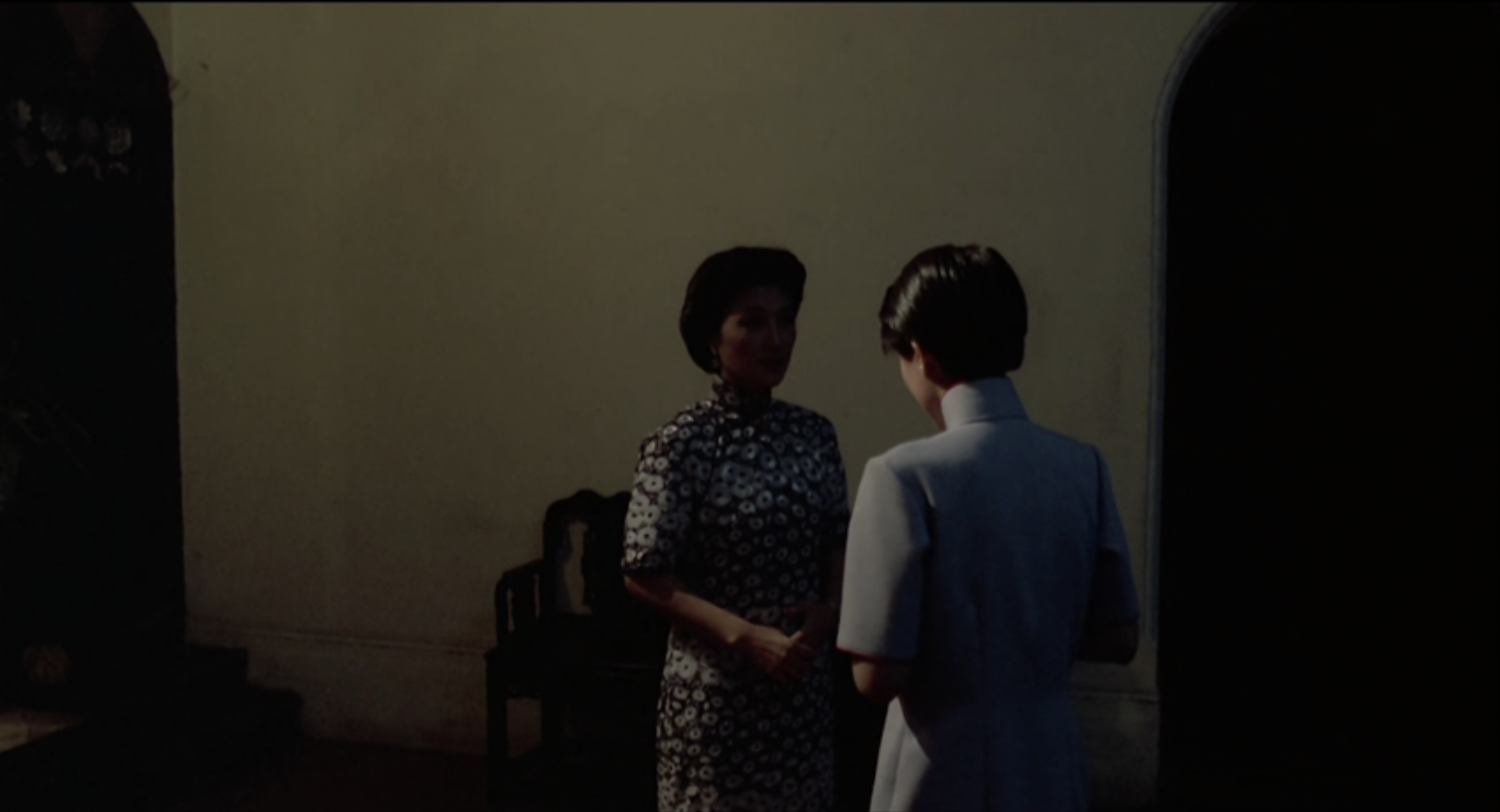

Allison Braden (AB): The film did strike me as a fascinating testament to the idea that extreme faithfulness can be, paradoxically, a detriment to adaptation. Conventional wisdom holds that books deal in emotions, plays in dialogue, and films in images. The limited visual scope of the first part of Love in a Fallen City—the repressively close Bai home, the tight shots in various hotel settings—calls to mind a teleplay, with more reliance on dialogue than images. This approach shortchanges Liusu’s interiority and writer Eileen Chang’s careful attention to emotional nuance. I spent the initial Hong Kong portion of the movie baffled by Liusu’s ambivalence. She clearly needs to escape her family but also seems determined to make a match for herself rather than meet anyone else’s expectations. “The first marriage is for your parents,” she says, “the second is for yourself.” But can she afford to dawdle? To repulse a supremely eligible suitor? Sure, Fan represented a foreign sensibility and exhibited domineering and misogynistic traits, but Liusu’s alternate reactions—charmed and put off—and quiet (is it too much to say sulky?) responses to his overtures didn’t offer a sufficient window into her feelings. The viewer is left to project her own interpretation on Liusu’s mystifying reticence, which I see less as intentional ambiguity and more as a failure to adequately adapt the interiority of the novel to a medium that relies on a different form of exposition. READ MORE…